Specifications
| Parameter | Details |
| Type | Press-in or Bolt-on, Load-Carrying/Follower |
| Stud Diameter | Commonly 14mm to 22mm |
| Material (Housing) | Forged Steel or Aluminum Alloy |
| Material (Stud/Ball) | Case-Hardened Chromoly Steel |
| Grease Fitting | Zerk Fitting Standard (for serviceable types) |
| Maximum Load Capacity | Up to 1500 kg static load |
| Operating Angle | ±30° from center |
| Seal Type | Synthetic Rubber Boot, Heat & Tear Resistant |
| Compatibility | Specific to vehicle make, model, and year |
| Warranty | Lifetime Limited Warranty on premium units |
These specifications ensure a precise fit and reliable performance. The load capacity and stud size are critical for matching vehicle weight and suspension dynamics. Always verify the exact type (load-bearing vs. follower) required for your specific application.
Applications
Ball joints are ubiquitous in the automotive world. They are a key component in the front suspension of nearly all passenger cars, SUVs, light trucks, and vans. In vehicles with independent front suspension systems—like those using MacPherson struts or double-wishbone setups—ball joints are essential for allowing the necessary wheel articulation during steering and over road imperfections.
Beyond standard road vehicles, heavy-duty ball joints are used in commercial trucks, buses, and agricultural equipment to withstand higher loads and rougher operating conditions. In the realm of performance and off-roading, upgraded, heavy-duty ball joints are crucial for lifted trucks, rock crawlers, and race cars, where extreme angles and impacts are common. They are also found in some rear suspension designs and in other mechanical linkages beyond automotive, such as in industrial machinery and aircraft control systems, showcasing their fundamental role in providing reliable, pivoting connections.
Advantages
- Precise Steering Response: Maintains accurate alignment and provides direct feedback for better vehicle control.
- Durability and Strength: Constructed from high-grade metals to endure shock loads and prevent failure.
- Reduced Friction: Precision-ground ball and socket with high-quality lubrication ensure smooth operation.
- Maintenance Options: Serviceable types with grease fittings allow for re-lubrication, extending service life.
- Safety Critical: A robust ball joint is vital for maintaining wheel attachment and overall suspension integrity.
- Wear Indicators: Many designs include visual or tactile indicators to signal when replacement is needed.
- Versatility in Design: Available in various sizes and configurations to fit a vast array of vehicle platforms.
- Improved Tire Life: A good ball joint helps maintain proper alignment, reducing uneven tire wear.
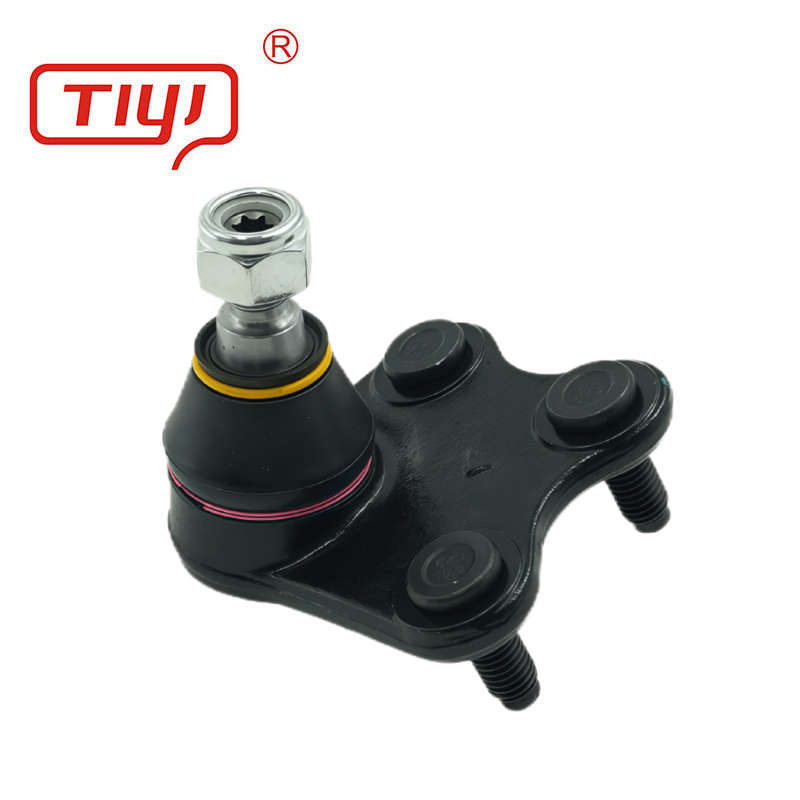
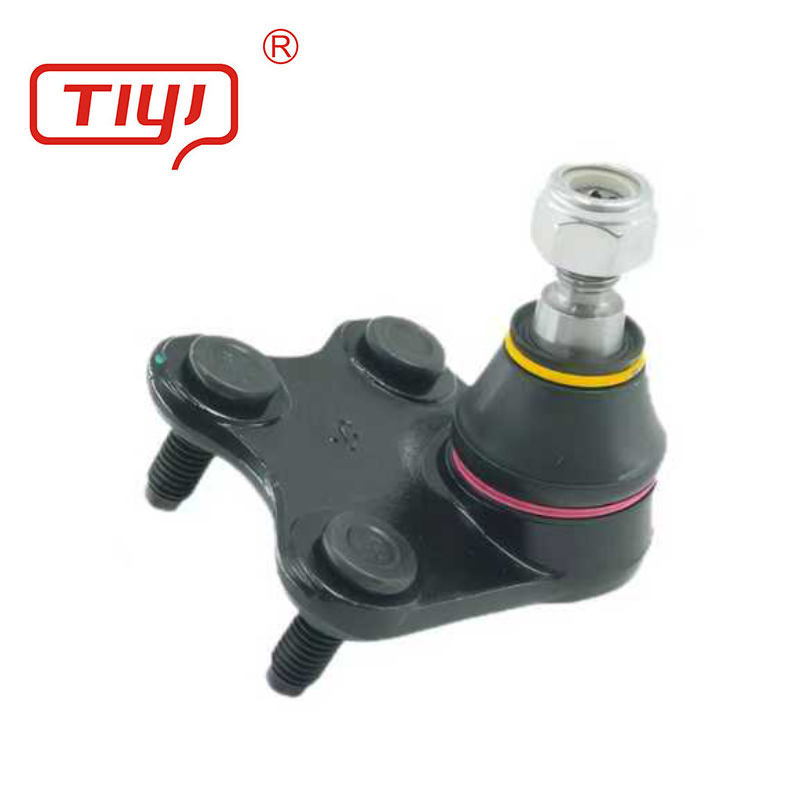
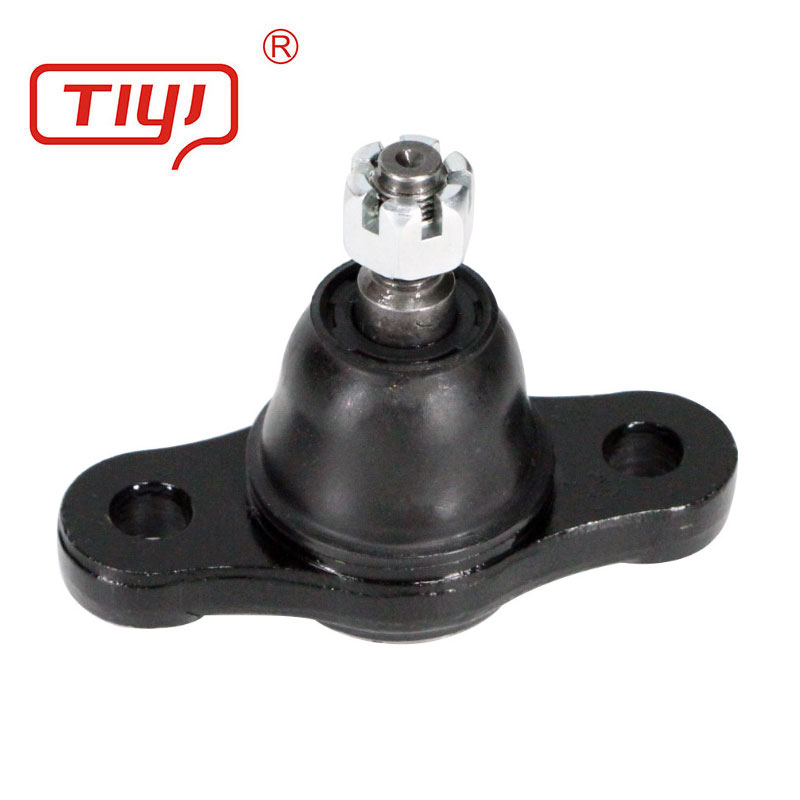
Materials and Structure
A ball joint is a marvel of mechanical simplicity and strength. The core component is a spherical bearing stud, typically made from case-hardened chromoly steel for a hard, wear-resistant surface and a tough core. This stud rotates and articulates within a precision-machined socket, often lined with a low-friction polymer or sintered metal bearing for smooth movement.
The housing or body is commonly forged from high-strength steel or machined from aluminum alloy for a balance of strength and weight. A critical part is the sealing boot, made from advanced synthetic rubber or polyurethane, designed to keep lubricant in and contaminants like dirt and water out. The internal cavity is packed with high-temperature, high-pressure grease. The assembly is often crimped or riveted together permanently, though some performance-oriented units are rebuildable. This construction ensures the joint can handle multi-directional forces while protecting its internal components from the harsh under-vehicle environment.