What is the relationship between Auto Stabilizer Link and Sway Bar?
 Administrator
Administrator
 2026-01-04
2026-01-04
The automotive suspension system is crucial for ensuring vehicle stability, handling, and comfort. Among its many components, the Auto Stabilizer Link and the sway bar (commonly known as the anti-roll bar) are key elements that work together to minimize body roll during cornering and maintain proper wheel alignment. Understanding their relationship helps drivers and automotive enthusiasts recognize the importance of these components in enhancing safety and performance.
Content
- 1 What is an Auto Stabilizer Link?
- 2 Understanding the Sway Bar (Anti-Roll Bar)
- 3 How Auto Stabilizer Link and Sway Bar Work Together
- 4 Comparing Auto Stabilizer Link and Sway Bar
- 5 Signs of a Failing Auto Stabilizer Link
- 6 Maintenance Tips for Optimal Performance
- 7 FAQs About Auto Stabilizer Link and Sway Bar
- 8 Conclusion
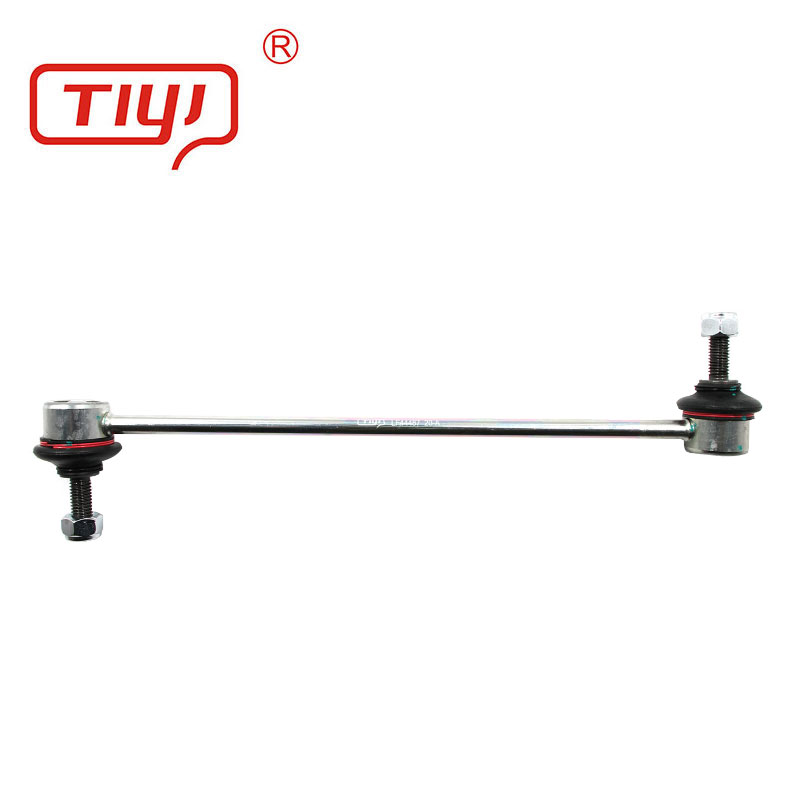
What is an Auto Stabilizer Link?
An Auto Stabilizer Link, also known as a sway bar link or end link, is a connecting rod that links the sway bar to the suspension components, typically the control arms or struts. Its primary function is to transfer forces from one side of the suspension to the other, ensuring that the sway bar can effectively reduce body roll and stabilize the vehicle during turns.
Key Functions of Auto Stabilizer Link
- Force Transmission: Transfers lateral forces between the sway bar and suspension components.
- Enhanced Stability: Helps maintain a level chassis during cornering or sudden maneuvers.
- Vibration Reduction: Absorbs minor shocks and prevents excessive movement in the suspension system.
- Longevity of Suspension Parts: Protects other suspension components by evenly distributing loads.
Understanding the Sway Bar (Anti-Roll Bar)
The sway bar is a torsional spring designed to reduce the vehicle's body roll when cornering. It is usually a U-shaped steel bar connected across the left and right sides of the suspension. By twisting under load, it balances the forces between both wheels and stabilizes the vehicle.
Main Advantages of a Sway Bar
- Reduced Body Roll: Minimizes leaning or tilting during turns, enhancing passenger comfort.
- Improved Handling: Ensures better grip and control by keeping tires more firmly on the ground.
- Enhanced Safety: Helps prevent oversteer or understeer situations by balancing lateral forces.
- Durability: Reduces stress on springs and shocks by sharing load across suspension components.
How Auto Stabilizer Link and Sway Bar Work Together
The Auto Stabilizer Link acts as the crucial connection point that allows the sway bar to function correctly. Without the stabilizer link, the sway bar would not be able to transfer forces efficiently, resulting in increased body roll and decreased vehicle control. Essentially, the link enables the sway bar to "communicate" with the suspension system, turning the twisting motion of the bar into balanced stabilization forces across the vehicle.
Functional Interaction
- During cornering, the suspension on one side of the vehicle compresses while the other extends. The sway bar resists this differential motion.
- The stabilizer link connects the sway bar to the suspension, ensuring that the torsional forces are properly transmitted.
- By linking both sides of the suspension, the vehicle maintains a flatter, more controlled posture, improving handling and passenger comfort.
Comparing Auto Stabilizer Link and Sway Bar
| Component | Primary Function | Impact if Faulty |
|---|---|---|
| Auto Stabilizer Link | Connects sway bar to suspension, transfers forces | Clunking noise, reduced handling, uneven tire wear |
| Sway Bar (Anti-Roll Bar) | Reduces body roll, balances lateral forces | Excessive leaning, compromised stability, oversteer or understeer |
In simple terms, the sway bar provides the stabilizing force, while the Auto Stabilizer Link acts as the intermediary that makes this force effective. Both are indispensable for achieving optimal vehicle handling.
Signs of a Failing Auto Stabilizer Link
Identifying issues with the Auto Stabilizer Link early can prevent damage to the suspension system and maintain vehicle safety. Common signs include:
- Unusual Noises: Clunking or rattling sounds, especially when driving over bumps.
- Reduced Stability: Increased body roll during turns or quick maneuvers.
- Loose or Worn Links: Visual inspection may reveal cracks, wear, or looseness.
- Uneven Tire Wear: Suspension misalignment caused by faulty links may accelerate tire wear.
Maintenance Tips for Optimal Performance
- Regularly inspect the Auto Stabilizer Link and sway bar bushings for wear or damage.
- Replace worn links promptly to avoid stress on the sway bar and other suspension components.
- Ensure proper torque settings during installation to prevent premature loosening.
- Use high-quality replacement parts to maintain stability and handling.
FAQs About Auto Stabilizer Link and Sway Bar
1. Can a car function without an Auto Stabilizer Link?
Technically, the vehicle can still move, but handling will be severely compromised. The sway bar cannot transfer forces properly, leading to increased body roll and reduced stability.
2. How often should Auto Stabilizer Links be replaced?
Replacement intervals vary depending on driving conditions, but generally, they last between 50,000 to 100,000 kilometers. Signs of wear or noise indicate the need for immediate replacement.
3. Are sway bars and stabilizer links the same thing?
No. The sway bar is a torsional rod that reduces body roll, while the Auto Stabilizer Link connects the sway bar to the suspension system, allowing it to function correctly.
4. What causes Auto Stabilizer Link failure?
Common causes include wear and tear, corrosion, heavy off-road usage, and poor-quality components. Replacing worn bushings and links prevents further damage to the suspension.
5. Can upgrading the sway bar improve handling?
Yes. A thicker or performance-oriented sway bar can reduce body roll further. However, the Auto Stabilizer Links must be compatible and strong enough to handle the increased force.
Conclusion
The relationship between the Auto Stabilizer Link and sway bar is a vital aspect of modern vehicle suspension systems. The stabilizer link acts as the bridge that allows the sway bar to perform its function, enhancing handling, reducing body roll, and ensuring passenger safety. Proper maintenance and timely replacement of these components are essential for optimal vehicle performance and driving comfort.





