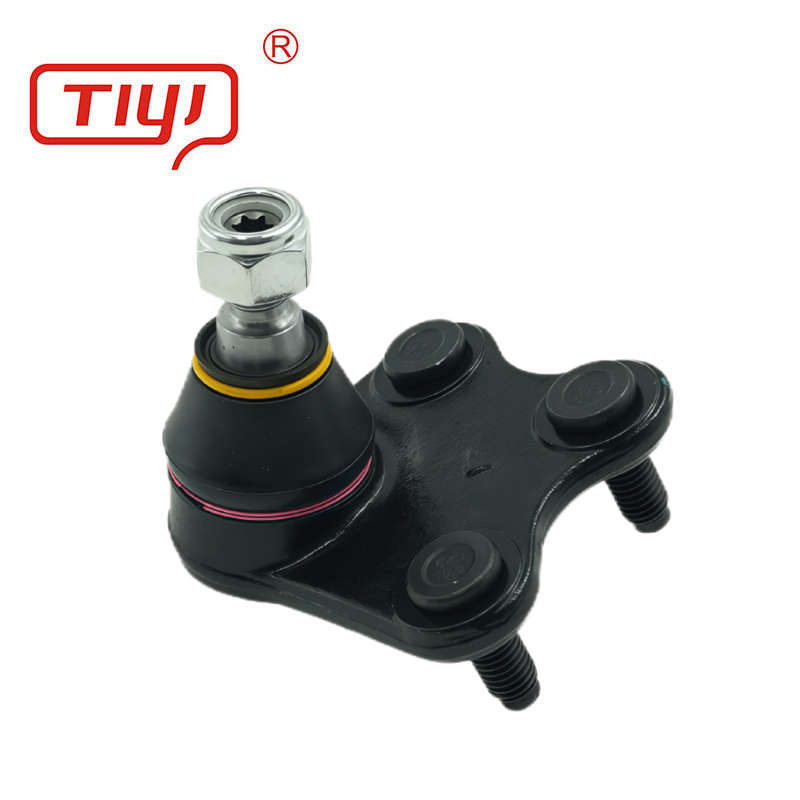
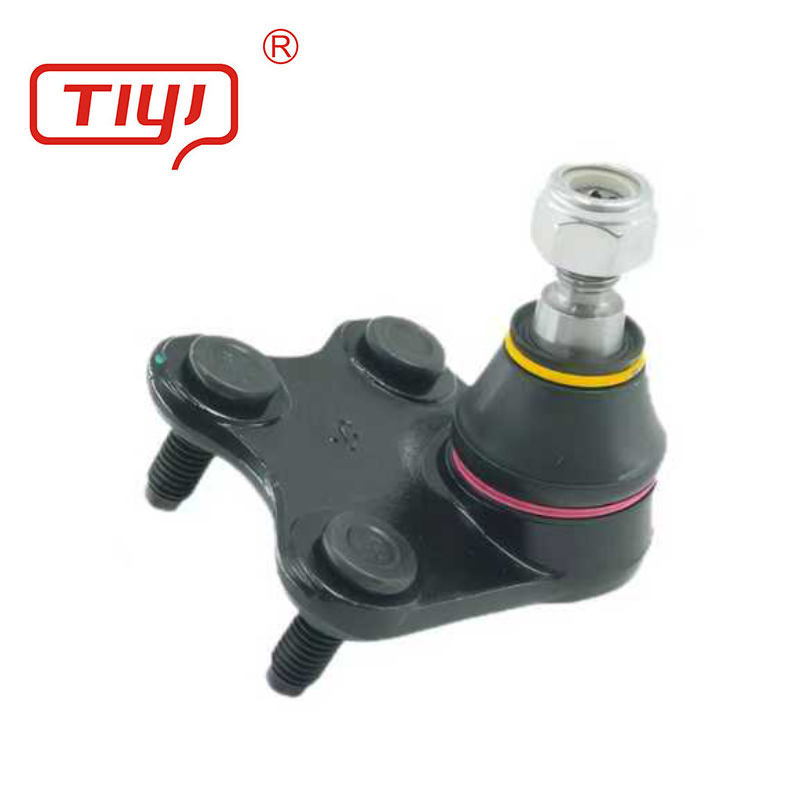
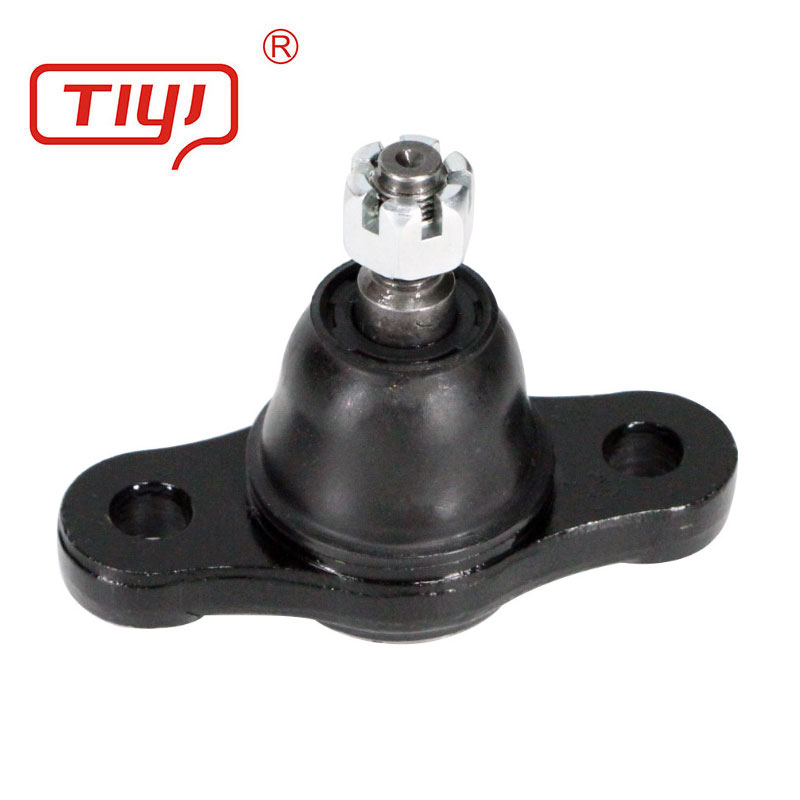
Specification
| Manufacturing & Capability Metric | Industry Standards & Benchmarks |
| Quality Management System | IATF 16949 Certification (Automotive Standard), ISO 9001, Compliance with SAE, DIN, JIS Specifications |
| Production Processes | Hot/Cold Forging, Precision Machining, Induction/Case Hardening, Automated Assembly, Robotic Welding |
| Material Specifications | SAE 8620, 4140, SCr420 Alloy Steels; Chromoly; HNBR/FKM for Boots; Specialized High-Temp Grease |
| Testing & Validation | Salt Spray Testing (500+ hours), Dynamic Fatigue Testing (100k+ cycles), Dimensional CMM Checking, Torque-to-Failure Testing |
| Product Range | OE (Original Equipment), IAM (Independent Aftermarket) Replacement, Performance, Heavy-Duty, Custom Designs |
| Technical Support | Engineering Catalogs, CAD Drawings, Installation Guides, Technical Bulletins, Field Application Support |
Applications
Ball joint manufacturers supply a global, multi-tier market. Their primary customer is the automotive Original Equipment (OE) sector, where they produce parts under contract for virtually every car and truck manufacturer. These parts are installed on new vehicles worldwide. A parallel and massive market is the Independent Aftermarket (IAM), where manufacturers produce replacement parts sold under their own brand or as private-label products through distributors, retailers, and repair shops.
Specialist manufacturers cater to niche segments: the performance racing market, providing uniball and high-angle joints; the heavy-duty truck and off-road sector, requiring oversized and reinforced joints; and the industrial/agricultural machinery industry, where similar pivot joint technology is used. Some manufacturers also offer complete assembly solutions, such as control arms with pre-installed ball joints, to simplify the repair process.
Advantages of Partnering with a Leading Manufacturer
- Assured Quality and Traceability: A certified manufacturer provides full traceability of materials and processes, ensuring every part meets published specifications and safety standards, minimizing the risk of defective products in the supply chain.
- Engineering Expertise and Innovation: Direct access to R&D capabilities means the manufacturer can develop improved designs—such as longer-life seals, easier installation features, or application-specific solutions—keeping pace with evolving vehicle technology.
- Comprehensive Product Coverage: Leading manufacturers maintain extensive, accurate application databases, ensuring availability of correct parts for a vast range of vehicles, which simplifies inventory management for distributors and shops.
- Supply Chain Reliability and Consistency: Robust manufacturing capacity and a controlled supply chain ensure consistent product availability, preventing business disruption due to part shortages or quality inconsistencies.
- Strong Technical and Warranty Support: Provides essential technical documentation, fitment support, and stands behind products with clear, strong warranty programs, reducing liability and building trust with channel partners and end-users.
- Customization and Special Order Capability: For unique applications (racing, restoration, prototyping), established manufacturers can often produce custom or small-batch parts to meet specific requirements.
Materials, Sourcing, and Production Philosophy
A quality manufacturer exerts strict control over its material supply chain. Studs and forgings are sourced from alloy steels with specific chemical compositions for optimal hardenability. Polymer compounds for bearing inserts are formulated for low friction and high wear resistance. Boot elastomers are selected for tear strength and environmental resistance.
The production philosophy centers on precision and repeatability. The stud is forged, machined, heat-treated (case-hardened), and ground to a precise spherical contour. The housing is forged or machined. The bearing assembly—whether PTFE-lined, sintered metal, or needle bearing—is assembled in a controlled environment with a precise amount of specialized grease. Critical processes like crimping or staking to retain the stud are automated and monitored. Each finished joint undergoes functional testing for smooth rotation, absence of play, and often, a check of breakout torque. The final step is applying a corrosion-resistant coating (e.g., zinc-nickel plating, e-coat) before packaging with clear identification.