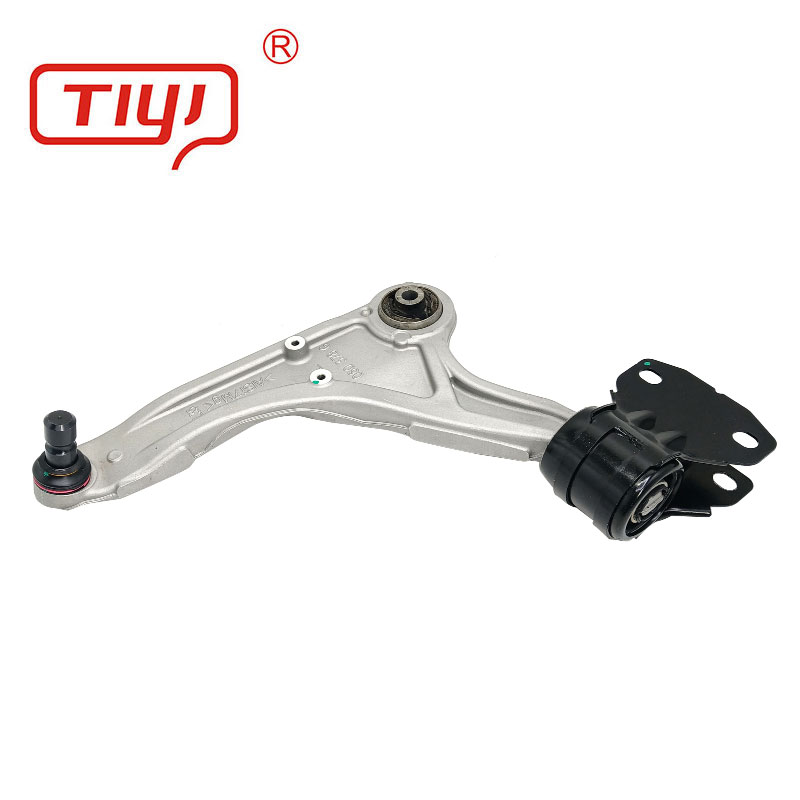
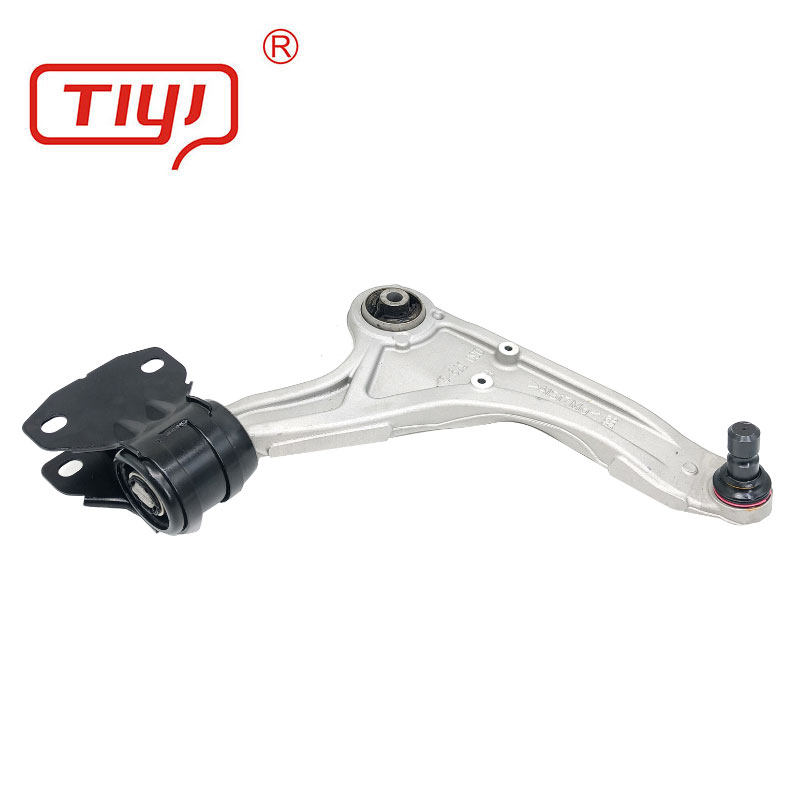
Specification
| Parameter | Typical Details |
| Bushing Type | Front Control Arm Bushing (Forward/Rear), Rear Control Arm Bushing, Trailing Arm Bushing, Clevis Bushing |
| Core Material | Natural/Synthetic Rubber, Polyurethane, Nylon, Spherical Bearing (Metal) |
| Durometer (Hardness) | Rubber: 60A-75A Shore; Polyurethane: 70A-95A Shore |
| Design Features | Solid, Voided (for specific compliance), Offset, Hydraulic (fluid-filled) |
| Inner Sleeve | Steel (plated), Aluminum, Delrin (for polyurethane bushings) |
| Dimensions | Outer Diameter: 40mm-80mm; Inner Diameter: 12mm-20mm; Width: 30mm-60mm |
| Load Rating | Engineered for vehicle-specific dynamic forces and weights |
Applications
Suspension arm bushings are used at every interface where a suspension arm pivots relative to the vehicle's body. In front suspensions, they are found in the forward and rear bushings of lower control arms in MacPherson strut systems, and in both upper and lower control arms of double-wishbone designs. Rear suspensions use them extensively in multi-link setups, trailing arms, and toe/camber adjustment arms.
Their application is universal across all vehicle types. Performance vehicles often use stiffer polyurethane bushings to sharpen handling response. Off-road vehicles may use harder durometer rubber or specialized designs to withstand greater articulation without tearing. Luxury vehicles might employ sophisticated hydraulic bushings for exceptional vibration isolation. During a full suspension refurbishment on any high-mileage vehicle, replacing all suspension arm bushings is a standard and transformative procedure.
Advantages
- Controls Suspension Geometry and Compliance:聽The bushing's stiffness and design dictate how the wheel moves under load, influencing critical handling traits like toe change during braking and cornering.
- Superior Vibration and Noise Damping:聽Effectively isolates high-frequency road imperfections and harshness, contributing significantly to cabin comfort and quietness.
- Absorbs Impacts and Shock Loads:聽Cushions the suspension arms and chassis from the direct force of potholes and bumps, protecting other components.
- Enhances Handling Stability and Feedback:聽Reduces unwanted deflection in the suspension linkage, providing more precise and predictable steering response.
- Extends Component Life:聽By absorbing shocks, they prevent metal-to-metal contact and reduce stress fatigue on the control arms and chassis mounting points.
- Maintains Wheel Alignment:聽Helps keep alignment settings stable by preventing excessive movement in the arm's pivot points.
- Tunable Performance:聽The availability of different materials and durometers allows enthusiasts to tailor the balance between ride comfort and handling sharpness.
Materials and Structure
Suspension arm bushings are precision-molded components. OEM rubber bushings are a blend of natural and synthetic rubber, vulcanized around a steel inner sleeve. Their structure often includes strategically placed voids or channels鈥攖hese are not flaws but engineered features that allow the bushing to flex more easily in certain directions, creating specific "compliance steer" characteristics desired by the vehicle's original designers.
Polyurethane bushings are molded from a dense polymer that is highly resistant to deformation, compression set, and environmental degradation (ozone, oil). They typically feature a low-friction inner sleeve made of Delrin (acetal resin). For the ultimate in precision with no compliance, spherical bearings (heim joints) can be used, replacing the elastic bushing with a metal ball-in-socket. Hydraulic bushings, used in some luxury cars, contain a glycol-based fluid within a rubber bladder to provide exceptional damping of small vibrations.