Specification
| Parameter | Details |
| Primary Material | Rubber (OE), Polyurethane, Nylon |
| Durometer (Hardness) | Rubber: 60A-75A; Polyurethane: 70A-95A |
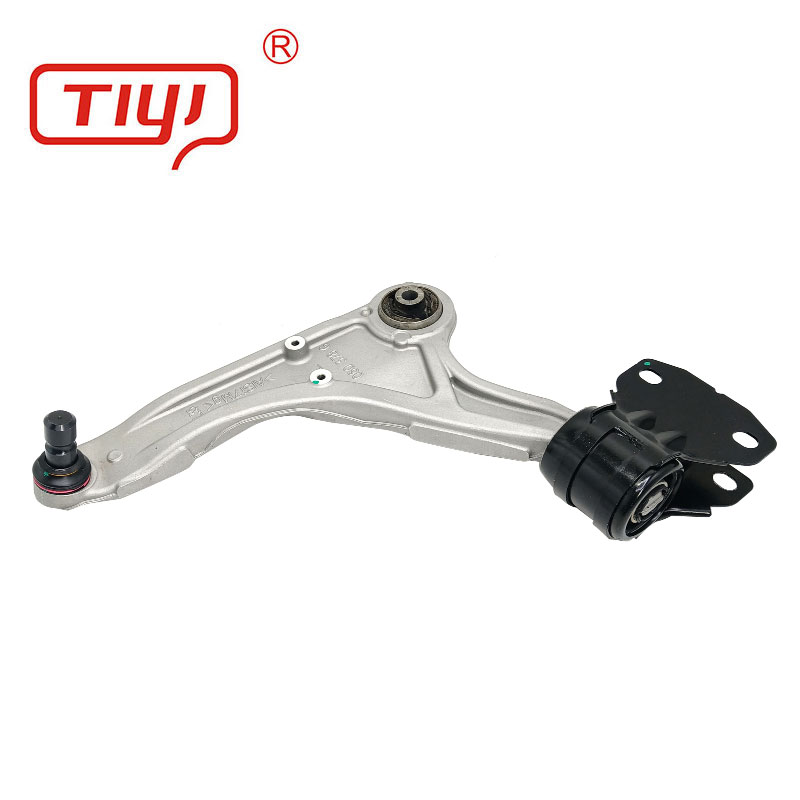
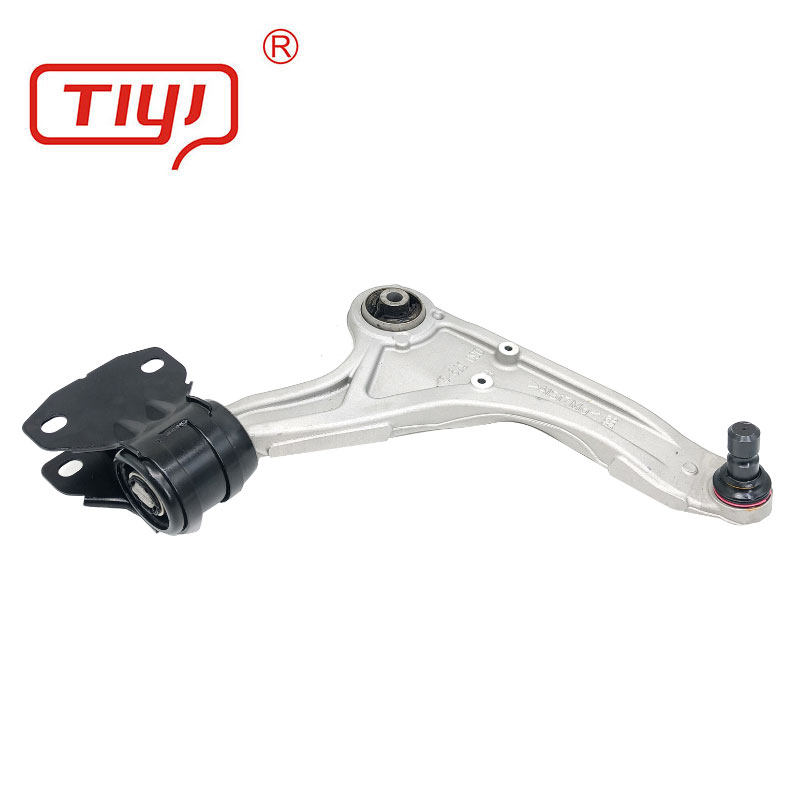
| Bushing Type | Front Lower Control Arm Bushing, Front Upper Control Arm Bushing, Rear Control Arm Bushing, Clevis Bushing, Offset Bushing |
| Design Features | Solid, Voided (for specific compliance), Hydraulic (fluid-filled) |
| Inner Sleeve Material | Steel (zinc-plated or powder-coated), Aluminum, Delrin |
| Dimensions (Sample) | Outer Diameter: 45-80mm; Inner Diameter: 12-20mm; Height: 30-60mm |
| Load Rating | Designed for vehicle-specific dynamic forces |
Applications
Control arm bushings are used at every point where a control arm connects to the vehicle's structure. In front suspensions, they are found in both the upper and lower control arms of double-wishbone and multi-link systems, and in the lower control arms of MacPherson strut designs. Rear suspensions on independent setups also utilize them extensively in trailing arms, lateral links, and toe links.
Their application is universal across all vehicle types—from compact cars to heavy-duty trucks. Performance and motorsport applications demand stiffer polyurethane or spherical bushings to minimize deflection during hard cornering, braking, and acceleration. Off-road vehicles benefit from heavy-duty bushings that can withstand extreme articulation without tearing. In classic car restoration, replacing the original, deteriorated rubber bushings is a foundational step in reviving the car's handling and ride.
Advantages
- Precise Suspension Control: Engineered compliance dictates the wheel's movement path, directly affecting camber and toe curves for optimal tire contact.
- Superior Vibration Damping: Effectively isolates high-frequency road vibrations and harshness, contributing to cabin comfort and quietness.
- Impact Absorption: Softens the blow from potholes and road imperfections, protecting other suspension components and the chassis.
- Enhanced Handling Stability: Reduces unwanted wheel movement under load, providing more predictable and confident cornering.
- Extended Component Life: By absorbing shocks, they protect the control arms, ball joints, and chassis mounting points from premature wear and fatigue.
- Alignment Preservation: Helps maintain proper wheel alignment settings by preventing excessive movement in the control arm pivots.
- Tunable Performance: Polyurethane bushings allow enthusiasts to choose a specific hardness to tailor the balance between comfort and handling sharpness.
Materials and Structure
Control arm bushings are meticulously engineered. OEM rubber bushings are typically made from a blend of natural and synthetic rubber, vulcanized around a steel inner sleeve. Their structure often includes strategically placed voids or channels. These voids are not defects; they are carefully designed to allow the bushing to flex more easily in certain directions, controlling the suspension's compliance characteristics—a concept known as "compliance steer."
Polyurethane bushings are molded from a dense polymer that is highly resistant to deformation, compression set, and environmental degradation. They usually feature a Delrin (acetal resin) inner sleeve, which provides a very low-friction surface against the mounting bolt. High-performance or racing applications may use spherical bearings (heim joints) at these points, which replace the compliant bushing with a metal ball-in-socket for zero deflection and maximum feedback, albeit with no vibration isolation.